-
Altera DE1-SoC
- VHDL
- Verilog
- SystemVerilog
-
STM32 Nucleo WB55RG
- STM32CubeMX
- mbedOS
- Online IDE (STM32CubeMX)
Morse code documentation
General explanation of how this simulation work
Download Word version Download Markdown versionMorse Code Simulation
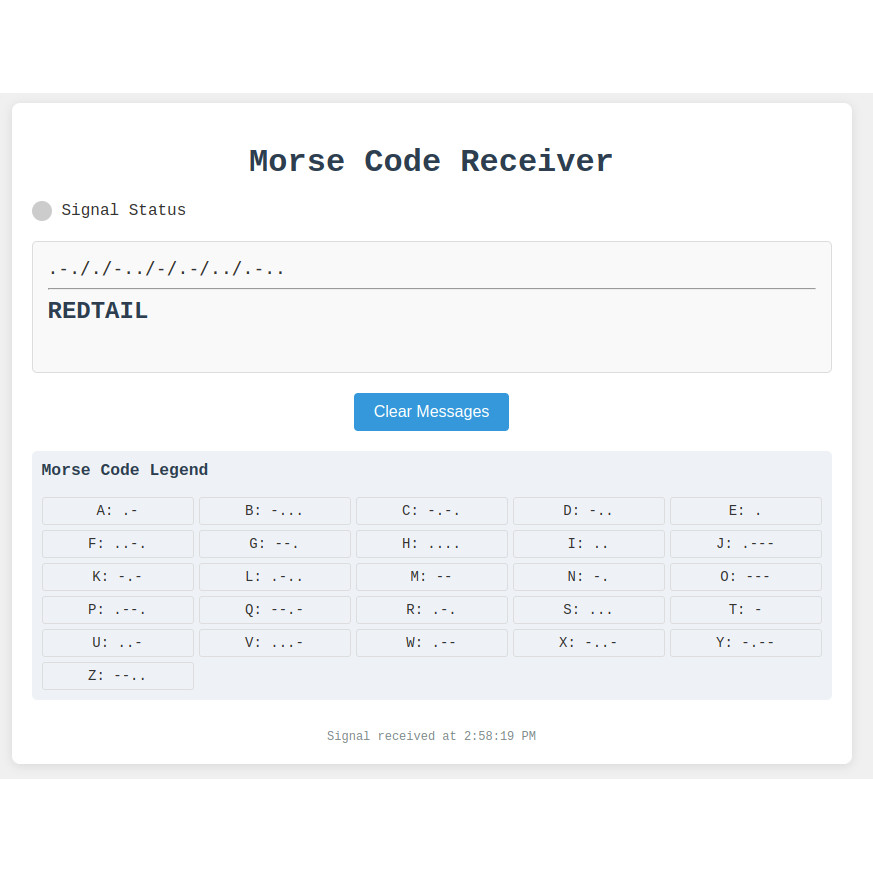
This project simulates Morse Code transmission and decoding. It processes binary input signals (. and -) in real-time, classifies them based on duration, and decodes them into corresponding alphanumeric and symbolic characters.
Overview
The system reads signal transitions (high/low) from a GPIO interface, calculates their durations, and interprets them as Morse symbols (dots, dashes, or spacing). These symbols are accumulated into a sequence and translated using a pre-defined Morse Code dictionary.
Features
- Morse Code Translation: Converts Morse Code signals: dots(
.), dashes(-), and spaces() into letters, numbers, and punctuation. - Speed Settings: Supports three speed modes (
Fast,Normal,Slow) with configurable thresholds for distinguishing between dots, dashes, letter gaps, and word gaps. - Signal Interpretation: Processes binary signals (high/low) based on their duration to determine Morse Code symbols.
- Dynamic Updates: Allows real-time updates to speed settings and clearing of the current buffer.
- Symbol Dictionary: Includes a full lookup table for alphabetic characters, numeric digits, and common punctuation symbols.
Speed Settings
The simulation supports three speed modes:
- Fast (F):
- Dot: 0.1 seconds
- Dash: 0.3 seconds
- Letter Space: 0.1 seconds
- Word Space: 0.3 seconds
- Normal (N) (default):
- Dot: 1.0 seconds
- Dash: 1.5 seconds
- Letter Space: 1.0 seconds
- Word Space: 2.0 seconds
- Slow (S):
- Dot: 3.0 seconds
- Dash: 5.0 seconds
- Letter Space: 3.0 seconds
- Word Space: 5.0 seconds
Morse Code Dictionary
The dictionary includes mappings for:
- Letters: A-Z
- Numbers: 0-9
- Punctuation: . , ? ' ! / ( ) & : ; = + - _ " $ @
Signal Processing
The simulation tracks high and low signals using timestamps and interprets their duration to determine the corresponding Morse Code symbol. It supports:
- Dots (.): Short high signals.
- Dashes (-): Long high signals.
- Letter Spaces (/): Short low signals.
- Word Spaces (): Long low signals.
How It Works
- Initialization:
-
The simulation initializes the Morse Code dictionary and sets default speed thresholds.
-
Signal Processing:
- Signals are read from the target device's GPIO pin (
morseSignal). -
The duration of each signal is measured and interpreted as a dot, dash, or space.
-
Translation:
-
Morse Code sequences are translated into human-readable text using the dictionary.
-
Dynamic Updates:
- Users can change speed settings or clear the current buffer in real-time.
Example Usage
Input Signals
- High signal (
1) for 0.1 seconds → Dot (.) - High signal (
1) for 0.3 seconds → Dash (-) - Low signal (
0) for 1.0 seconds → Letter Space (/) - Low signal (
0) for 2.0 seconds → Word Space ()
Output
- Input:
.-- --- .-. -.. / - . ... - - Output:
WORD TEST